Change Implementation Techniques for Forming Transitional Team, Creating Alignment, Maximizing Connectedness and Creativity
Technique 6.18 Random Word - A Chance Method of Po
This random word strategy is used to open up new ideas around a chosen focus ‐ it has no apparent connection with the situation, and appears illogical and completely unworkable.
Random word is based on the principle of priming which is using a mechanism of association, ie a word or concept is used to prime other ideas. Priming refers to the influence of an action by a word or idea.
The concept is based on the notion that if you start at the periphery you are likely to open up patterns which are not dominated by the central starting point.
Furthermore, the more remote the random word is from the problem the better, as it stimulates thinking along entirely new lines.
This is most powerful once you have hit the "brick wall".
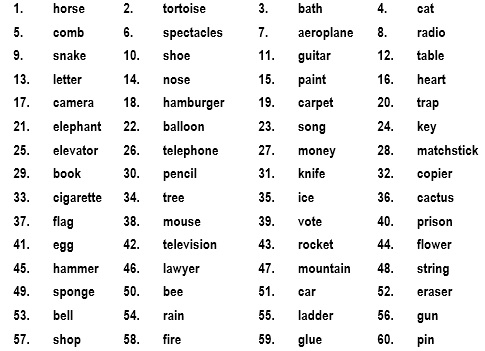
Use the second hand of your watch to select a word from the list of 60 words:
List Of Random Words
An example of using random word:
random word (#56) - "gun"............................as the predominately Chinese audience attending Edward deBono's presentation in Singapore were reluctant to ask questions like Western audiences, he used the random word "gun". You point a gun at a target; thus, he had all the chairs numbered. When it came to question time, he would call out a number and the attendee with the number would give their comments.
Alternatives to lists of words can be sourced from a dictionary (use nouns only), newspaper and picture cards
(sources: Edward deBono, 1992; Peter Drucker, 2001)
Six More Examples of Random Word Use
i) How to improve leadership by using random word "tortoise" (#2)
Hard shell, ie leader needs to be hard within him/herself to cope with flak from workers and directors. At the same time,
- it has a hard exterior but soft interior, ie can handle "hard" and "soft" issues
- can come out of shell and is ready for action when steady influence is needed.
Versatile, ie can handle different environments (water/land) ‐ slow on land and fast in water
Long life, ie looking at long-term goals
"Slow" and steady but consistent and gets job done
Calm, ie not hot-headed
Can return to shell, ie leave teams to be self-managed
Self-assured, ie puts the foot in the right spot every time
Vulnerable and helpless, ie if tortoise is on his back
(source: Nolan Meats, 2001)
ii) How to eliminate paperwork by using random word "cactus" (#36)
6 steps to every deal
C orrect (do it correctly)
A daptation
C ollection of information
T echnology
U nderstand
S implicity
Correct adaptation through the use of collection of information utilising the new technology to understand and to achieve simplicity
Cactus grows in the desert where trees don't grow - hence no paper
Cactus spikes paper on spike but now with computers no spikes no paper
Cactus ‐ able to use limited resources available in the desert
Cactus makes efficient use of available resources
Cactus can withstand harsh environment survivor
(source: Xerox/NEC Business Centres, 2000)
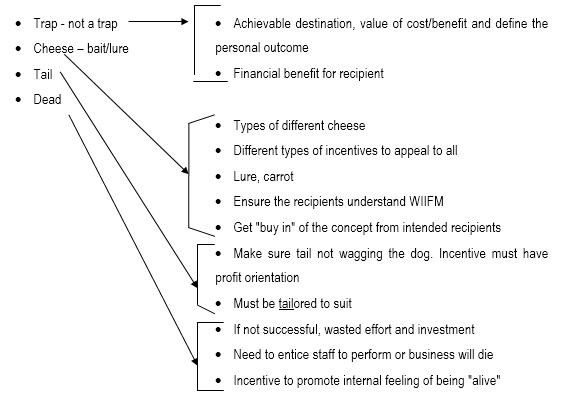
iii) Looking at incentives for staff by using random word "mouse" (#38)
source: Xerox/NEC Business Centres, 2000)
iv) How to improve team communications by using random word "mountain" (#47)
Get lots of views, ie mountains of views
Gather views at different levels
Good communications at all levels as you go up the mountain
At the top of the mountain you get a better view
Better view of where you've come from and where you are headed
Steps to climb to top
Do we have a safety rope?
Need to make sure that we have firm foundations
Solid leadership base required as no good building on a soft base
Stop on plateau to get direction, ie proceed if going well while if not, may need re-work
King of mountain to guide people (team members) up the steps
Is it too big to climb?
Building steps, ie find where to start
Gradual climb and don't take hardest part first, ie "by the mile it's hard, inch by inch it's a cinch"
Foundations - are they firm?
Are the steps disappearing behind us? ie are we climbing and no-one is following?
Stop on plateau, ie don't keep going if the team isn't coming with you
(source: Nolan Meats, 2001)
v) How to improve team motivation by using random word "flag" (#37)
vi ) How to improve business performance by using the random "snake" (#9)
Lives in cool, background places ‐ also, snakes live in the background meaning they work effectively on 'cool' things and do not communicate loudly ‐ can still be effective quietly.
Wriggles ‐ operates below the radar; also symbolizes restlessness, which can mean a desire for continuous improvement; has "up and downs"
Many colours ‐ ability to adapt to change
Swims, crawls ‐ no barriers, looks beyond the comfort zone to get the job done
Considered 'wise' ‐ knows when to act/speak/execute/keep in the background
Is 'feared' ‐ generates respect through perception management
Long and lean ‐ think long-term, operate lean to react faster
Sheds its skin very year ‐ re-invents itself annually
Hibernates ‐ when environment not receptive, disappears; when environment receptive, comes to life
Can poison or strangle prey ‐ lethal to competition
Mongoose can handle snakes ‐ its "Achilles Heel"
Game of snakes and ladders ‐ knows when to go up and down
Stalks prey (once located tracts that prey use, waits in hiding for prey to ambush it) ‐ planned opportunism
(source: Eugene Singh, 2009)